We provide Comp Organization Architecture online (apkid: com.nupuit.computerorganizationanda) in order to run this application in our online Android emulator.
Description:
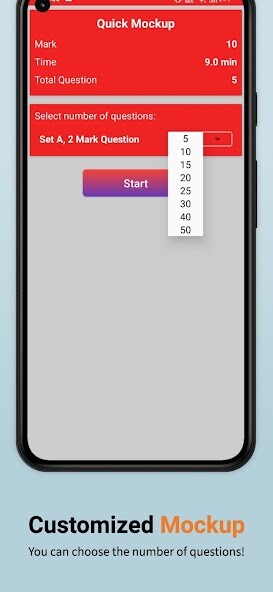
Run this app named Comp Organization Architecture using MyAndroid.
You can do it using our Android online emulator.
Computer Organization and Architecture Exam Prep
Key Features of this APP:
At practice mode you can see the explanation describing the correct answer.
Real exam style full mock exam with timed interface
Ability to create own quick mock by choosing the number of MCQs.
You can create your profile and see your result history with just one click.
This app contains large number of question set that covers all syllabus area.
The first documented computer architecture was in the correspondence between Charles Babbage and Ada Lovelace, describing the analytical engine.
When building the computer Z1 in 1936, Konrad Zuse described in two patent applications for his future projects that machine instructions could be stored in the same storage used for data, i.e.
the stored-program concept.
Two other early and important examples are:
John von Neumann's 1945 paper, First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC, which described an organization of logical elements;and
Alan Turing's more detailed Proposed Electronic Calculator for the Automatic Computing Engine, also 1945 and which cited John von Neumann's paper.
The term architecture in computer literature can be traced to the work of Lyle R.
Johnson and Frederick P.
Brooks, Jr., members of the Machine Organization department in IBMs main research center in 1959.
Johnson had the opportunity to write a proprietary research communication about the Stretch, an IBM-developed supercomputer for Los Alamos National Laboratory (at the time known as Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory).
To describe the level of detail for discussing the luxuriously embellished computer, he noted that his description of formats, instruction types, hardware parameters, and speed enhancements were at the level of system architecture a term that seemed more useful than machine organization.
Subsequently, Brooks, a Stretch designer, started Chapter 2 of a book (Planning a Computer System: Project Stretch, ed.
W.
Buchholz, 1962) by writing,
Computer architecture, like other architecture, is the art of determining the needs of the user of a structure and then designing to meet those needs as effectively as possible within economic and technological constraints.
Brooks went on to help develop the IBM System/360 (now called the IBM zSeries) line of computers, in which architecture became a noun defining what the user needs to know.Later, computer users came to use the term in many less-explicit ways.
The earliest computer architectures were designed on paper and then directly built into the final hardware form.Later, computer architecture prototypes were physically built in the form of a transistortransistor logic (TTL) computersuch as the prototypes of the 6800 and the PA-RISCtested, and tweaked, before committing to the final hardware form.
As of the 1990s, new computer architectures are typically "built", tested, and tweakedinside some other computer architecture in a computer architecture simulator; or inside a FPGA as a soft microprocessor; or bothbefore committing to the final hardware form.
Key Features of this APP:
At practice mode you can see the explanation describing the correct answer.
Real exam style full mock exam with timed interface
Ability to create own quick mock by choosing the number of MCQs.
You can create your profile and see your result history with just one click.
This app contains large number of question set that covers all syllabus area.
The first documented computer architecture was in the correspondence between Charles Babbage and Ada Lovelace, describing the analytical engine.
When building the computer Z1 in 1936, Konrad Zuse described in two patent applications for his future projects that machine instructions could be stored in the same storage used for data, i.e.
the stored-program concept.
Two other early and important examples are:
John von Neumann's 1945 paper, First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC, which described an organization of logical elements;and
Alan Turing's more detailed Proposed Electronic Calculator for the Automatic Computing Engine, also 1945 and which cited John von Neumann's paper.
The term architecture in computer literature can be traced to the work of Lyle R.
Johnson and Frederick P.
Brooks, Jr., members of the Machine Organization department in IBMs main research center in 1959.
Johnson had the opportunity to write a proprietary research communication about the Stretch, an IBM-developed supercomputer for Los Alamos National Laboratory (at the time known as Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory).
To describe the level of detail for discussing the luxuriously embellished computer, he noted that his description of formats, instruction types, hardware parameters, and speed enhancements were at the level of system architecture a term that seemed more useful than machine organization.
Subsequently, Brooks, a Stretch designer, started Chapter 2 of a book (Planning a Computer System: Project Stretch, ed.
W.
Buchholz, 1962) by writing,
Computer architecture, like other architecture, is the art of determining the needs of the user of a structure and then designing to meet those needs as effectively as possible within economic and technological constraints.
Brooks went on to help develop the IBM System/360 (now called the IBM zSeries) line of computers, in which architecture became a noun defining what the user needs to know.Later, computer users came to use the term in many less-explicit ways.
The earliest computer architectures were designed on paper and then directly built into the final hardware form.Later, computer architecture prototypes were physically built in the form of a transistortransistor logic (TTL) computersuch as the prototypes of the 6800 and the PA-RISCtested, and tweaked, before committing to the final hardware form.
As of the 1990s, new computer architectures are typically "built", tested, and tweakedinside some other computer architecture in a computer architecture simulator; or inside a FPGA as a soft microprocessor; or bothbefore committing to the final hardware form.
MyAndroid is not a downloader online for Comp Organization Architecture. It only allows to test online Comp Organization Architecture with apkid com.nupuit.computerorganizationanda. MyAndroid provides the official Google Play Store to run Comp Organization Architecture online.
©2024. MyAndroid. All Rights Reserved.
By OffiDocs Group OU – Registry code: 1609791 -VAT number: EE102345621.